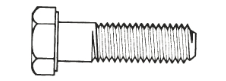
Hex Bolts & Hex Cap Screws
Hex bolts feature a large head for distributing clamping load, along with a partial external thread. Hex bolts can be used at high temperatures and high pressures. Hex cap screws are a form of hex bolts that have a washer face underneath the head and are used in precise applications. Heavy hex head bolts can be used for structural connections in wind turbines, commercial solar arrays, buildings, bridges, and railways.
Grade 2 o Grade 5 o Grade 8
While some smaller bolts aren't typically graded, meaning their strength isn't specified, larger bolts and those for specialized purposes are made to meet certain strength requirements. American standard fasteners will have a grade or ASTM rating, while Property class (usually just referred to as "class") is used to specify the strength of metric fasteners. Special markings on the heads of bolts can be used to identify the fastener's grade. For more information, click here to see our Bolt Head Identification Chart.
Tap Bolts (Full Thread)
As opposed to a standard hex bolt, a tap bolt is hex bolt that is fully threaded. While a hex cap screw is not necessarily fully threaded, they are available in fully threaded versions. Hex tap bolts are often threaded into something such as a piece of machinery, rather than being used with a nut.
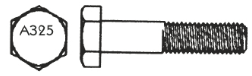
A325 Structural Bolts
Prior to its withdrawal in 2016, the ASTM A325 specification covered high strength heavy hex structural bolts from 1/2″ diameter through 1-1/2″ diameter. A325 structural bolts are intended for use in heavy duty structural connections and have shorter thread lengths than standard hex bolts. The A325 specification is applicable to heavy hex structural bolts only. For bolts of other configurations and thread lengths with similar mechanical properties, see Specification A449.
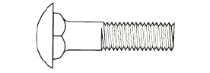
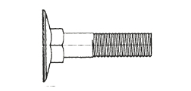
Carriage Bolts
A carriage bolt features a square shoulder under a rounded head which resists turning when the nut is tightened or removed. This makes carriage bolts good for wood-to-wood connections when the head may not be accessible for tightening. Carriage bolts can also be used in the construction of docks, swing sets, decks any any surface where a smooth finish is important.
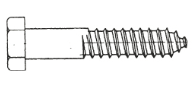
Lag Screws (Hex Lag Bolts)
Lag screws, also known as lag bolts, are used in wood construction for heavier load applications than most wood screws can support. Lag screws can also use a nut to add extra strength and security when holding things together. Once one is installed, it takes a brunt of the weight and removes it from the structure itself. You'll often see lag screws in solar installations, on patios, decking and other construction uses.
Elevator Bolts
Elevator bolts are often used to hold together belts in machine conveyer systems. The large diameter of the head and square neck creates a greater bearing surface to stop the bolt from going through the soft conveyer material. Elevator bolts can be used in any application where a low profile head is of utmost importance.
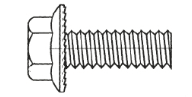
Serrated Flange Bolts
Armed with teeth-like serrations, serrated flange bolts are one-piece bolts bite into surfaces to resist vibration. This bolt is identifiable by the ridge or surrounding the bolt head, this built-in washer under the head of the bolt acts to distribute the clamping load over a greater area. A flange bolt is designed to provide the same holding power as a washer.
Hanger Bolts
Hanger bolts have different threaded areas at either end: a lag screw thread at one end and machine screw thread on the other. Hanger bolts are designed to be inserted into a pre-drilled hole and are ideal for use in rooftop and overhead applications, such as rooftop solar panel installation and suspending electrical wiring or sheet metal from wooden structures.
Studs
As opposed to threaded bolts, studs have no head and are threaded along their entire length. Additionally, studs generally have a higher tensile strength than threaded bolts. Fully threaded studs are usually fastened with two nuts and used in machinery and other objects that must be assembled and dissembled quickly.
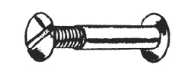
Sex Bolts
A sex bolt is a mating fastener combining a nut and a screw. The sex bolt consists of a female internally threaded barrel nut and a male externally threaded screw. Both the barrel and screw have heads designed to clamp material between the head of the barrel and the head of the screw, or to bridge the gap between two parts.